What is an ear infection?
Infections of the inner ear (otitis media) and outer ear (otitis externa) are two of the most common reasons for clinic visits in both children and adults. Inner ear infections occur when fluid builds up in the area behind the eardrum and then becomes infected, typically with bacteria. Outer ear infections, often called Swimmer’s Ear, occur when the ear canal, which is the passage between the outer ear and the eardrum, becomes infected and inflamed.
What causes ear infections?
Inner ear infections often occur as a result of a viral infection such as a cold or other upper respiratory infection including COVID-19. They are very common, especially in children, because their shorter, more horizontal eustachian tubes allow bacteria and viruses to find their way into the middle ear more easily than in adults. Children’s eustachian tubes are also narrower which means that they are more likely to get blocked. COVID-19 can also cause congestion and fluid buildup in the ears and lead to an ear infection.
Outer ear infections can occur because of excess moisture or because of an injury such as a cut or scrape to a person’s outer ear that later becomes infected.
What are the symptoms of ear infections?
Common symptoms of inner ear infections include ear pain, fever, fluid drainage from the ear, temporary hearing loss, and trouble eating, drinking, or sleeping. Young children may pull or tug at the affected ear more frequently. Chewing, sucking, and lying down can cause painful pressure changes in the middle ear. Chronic inner ear infections in children are sometimes treated by a doctor placing very small plastic tubes in the child’s ears to allow fluid or pus to drain.
Symptoms of outer ear infections include ear pain, itchiness in the ear canal, swelling of the ear canal, a discharge of liquid or pus from the ear, and temporary hearing loss.
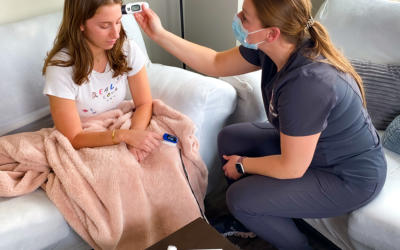
How will your Pivotal Health diagnose and treat your ear infection?
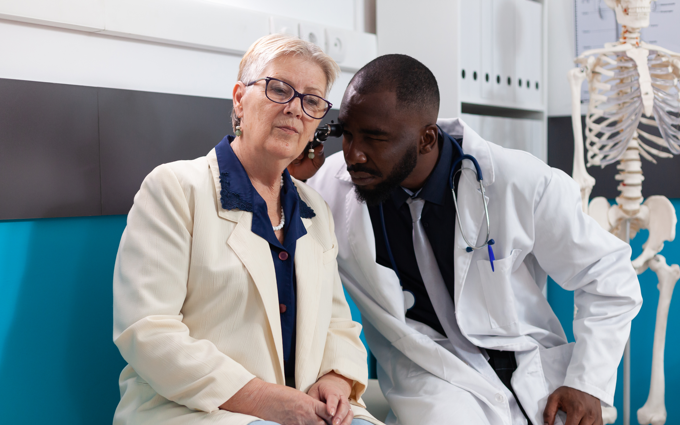
Because symptoms of inner and outer ear infections can mimic symptoms of other conditions, it’s important to seek medical attention to get an accurate diagnosis and ensure proper treatment. Ear infections are one of the most common conditions that Pivotal Health treats. If you suspect that you or a loved one might have an ear infection, don’t hesitate to schedule a Pivotal Health house call. The Pivotal Health clinician will perform a complete examination, including a full check of the patient’s ears, nose, and throat, and determine if the symptoms indicate an ear infection. They use an otoscope – a small, magnified instrument similar to a flashlight – to see the ear canal and eardrum.
The Pivotal Health clinician will then provide a comprehensive treatment plan to manage pain and other symptoms. The clinician will consider many factors when creating a treatment plan; including the type and severity of the infection, how often the patient has ear infections, how long the infection has lasted, the patient’s age and any other risk factors that may be present.
For outer ear infections, antibiotic or topical steroid ear drops are often prescribed. For inner ear infections, antibiotics are not always needed. If the Pivotal Health clinician deems antibiotics necessary, they can easily send a prescription electronically to your preferred pharmacy.
What are the risks of not treating your ear infection?
Some ear infections, if left untreated, may resolve spontaneously if the infection is related to a viral illness. Others may progress to worsening symptoms and worsening infection. Like many other infections, if left untreated, ear infections may progress to other areas of your body such as surrounding tissues or bones. Leaving an ear infection untreated may also negatively affect your hearing, potentially resulting in permanent hearing loss or damage.
How can you care for yourself at home?
- Take over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen, to reduce pain, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen) to reduce pain and inflammation
- Apply a warm compress to the affected ear to help facilitate fluid drainage
- Utilize an over-the-counter nasal spray, such as saline or sodium chloride
When should you seek emergency care for your ear infection?
- You have a fever greater than 101.5 degrees Fahrenheit, even with the use of fever reducing medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- You suffered a head injury recently and have blood draining from your ears
- You have lost hearing completely
How can you prevent an ear infection from recurring?
- Be sure that you and your children are up to date with all recommended vaccines
- Ensure ear canals are dry after you or your child swims or showers
Help for Ear Infections from Pivotal Health
If you’re experiencing symptoms of an ear infection, connect with Pivotal Health to discuss your potential treatment options based on your symptoms. Our experienced triage support and clinicians will help you determine if you need emergency care or can be seen in the comfort of your home, on your own schedule, by a licensed Pivotal Health provider.
Pivotal Health clinicians can diagnose ear infections, recommend non-pharmacologic interventions, prescribe medications if necessary, and create a treatment plan for you. All Pivotal Health clinician visits, including for ear infections, include follow-up consultation to ensure you’re on the road to recovery.